- Home → Archive: July, 2017
A Comprehensive Guide to Forex Brokerage
1. INTRODUCTION
Are you thinking to start trading in forex market or already in forex trading? Well, in both the cases choosing a trusted forex broker is important. It is difficult to find a reliable forex broker if you do not have sound knowledge about it.
Since forex brokerage is way too complicated to the average prospective client, this fact places most would-be clients in very precarious situations. Plenty of time and business opportunities are often wasted. More often than not, wrong decisions are also made. It is therefore imperative for all and sundry to familiarize them with the entire gamut of forex brokerage.
This article entitled, “A Comprehensive Guide to Forex Brokerage” endeavors to demystify this subject matter and aid clients in finding a trusted broker. It accomplishes this by investigating and explaining in great details the various aspects of the subject matter.
1. WHAT IS A FOREX BROKER?
For a start, the term Forex Trading refers to the global decentralized or over-the-counter exchange of foreign currencies i.e. the buying, selling or the exchange of currencies at current rates or determined prices.
A forex broker is basically a firm which provides currency traders, and other stakeholders in the field of currency trading with the access to a trading platform which subsequently allows them to buy or sell foreign currencies. They mainly facilitate the activities of retail forex brokers/currency trading brokers by granting them 24-hour access to the currency market.
2. Why do you need trusted broker?
To trade successfully in forex market without having any interruption, a trader has to get a trusted broker. To be failure in selecting right broker means to go ahead in the failure mission of forex trading. Since forex issues deal with your hard earned cash, it is wise to make sure the person whom you choose to put in charge of your money is regulated, honest and trustworthy. You can not actually understand that the broker is scamming your money in guise. As the retail traders trades via online, it is difficult to find out the right broker if you do not have sufficient knowledge about forex brokerages and their functions.
A trader needs to keep a couple of things in consideration when he tries to choose best forex broker to trade in. The article covers INS and outs of forex brokerage that a trader must know.
3. HOW DOES A FOREX BROKER WORK?
Forex brokers work primarily by buying and selling foreign currencies from corporate and individual clients. They buy the currency at a cheaper price than they eventually sell them. This means that they derive some profit in the course of trading. This profit is technically called a “spread”, and it is the incentive that keeps forex brokers in the business. Some may also charge commission on every transaction process as a way of shoring up their revenue base.
Apart from the buying and selling of foreign currencies, forex brokers also offer the following services/benefits to their clientele:
• Leverage – This is a special type of loan that forex brokers advance to repeat clients and regular customers.
• Liquidity – It refers to the amount of liquid cash that is at the disposal of the economy at any given time. Owing to the fact that the primary objective of forex trade is the exchange of currencies, it follows that they play a crucial role in availing enough liquidity.
• Safety/Security – Forex brokers also help in curbing money laundering and the counterfeiting of currency notes since they have scanners and special equipment that can detect such problems.
• Credit Referencing – Regular and repeat clients have the added benefit of being able to be referenced or recommended for loans from any financial institution.
4. TYPES OF FOREX BROKERS
Forex brokers exist in various shapes and forms. Below are some of the most notable types of forex brokers:
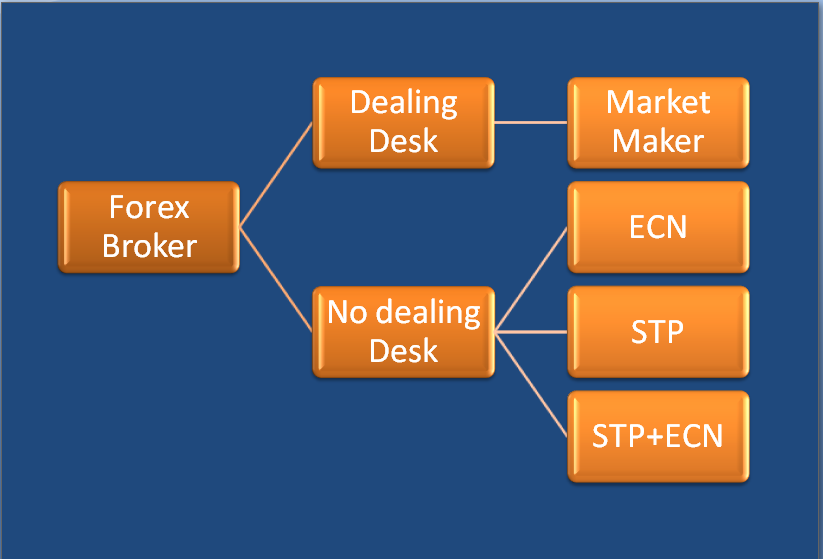
4.1 Dealing Desk broker
They primarily create markets/sales leads for their clients. It is also called market maker broker they do so in return for a spread that arises due to the differences in the buying and the selling prices. They provide traders with buy and sell quotes besides providing liquidity to their clients. Trading using a dealing desk broker basically entails placing a trading order on a trading platform. The order is then picked up by a dealing desk broker who in turn uses it to win trades of clients.
| Pros | Cons |
| Your Trades will be executed at your selected rate | Prices may differ slightly from interbank |
| Fixed Spread- You knows before how much you will pay to your broker. | You may face low liquidity problem at times when your broker can not find counterparties for your trades |
| Wide range of leverages – for those with a healthy risk appetite these can go up to 1 x 500 with some brokers. You may get wide range of leverage. You may get 1*500 or more leverage | There is risk that the broker may go bankrupt if the dealing desk isn’t managed correctly. There is a risk in dealing desk broker. The broker may go bankrupt if they are not managed correctly |
4.2 NDD (No Dealing Desk)
It is a system of forex trading which provides direct and immediate access to interbank markets where foreign currencies are traded. It also allows for direct contact with the market liquidity providers as it eliminates the need for intermediaries as is the case with the dealing desk brokers. The system may accommodate several liquidity providers at a time and hence enables the forex brokers to obtain the most competitive bids and ask prices besides granting the investors access to instant executable rates.
4.2.1 ECN
ECN stands for Electronic Communications Network. ECN brokers are those that employ electronic communication networks to provide their clients direct access to the other participants in the trade of currency. They do this by consolidating price quotations from several market participants and channeling the same to all the other participants. They generally offer their clients tighter bids and receive higher spreads as compared to the dealing desk brokers. ECNs cannot take a direct part in the trade of foreign currency since they merely act as intermediaries in the entire process.
4.2.2 STP
The initials STP stand for Straight through Processing and refer to those brokers who receive client orders and pass them directly to the liquidity providers such as banks, hedge funders, investments corporations, or other brokers. They eliminate other intermediaries in the brokerage chain of command, minimize delay in the processing of orders, negate the need to resend quotes to clients and allow clients to trade instantly. They mainly transact with banks given the fact that they generally trade on the interbank markets.
4.5 DMA = Direct Market Access
It is an electronic trading facility that grants investors intending to deal in financial instruments a way of interacting with the order books of an exchange. The electronic facility is often provided by independent firms and empowers the buy side firms to have greater controls over the manner in which their trade is executed. The use of this facility greatly minimizes errors, expedites the process of forex trading, and allows traders to leverage the benefits of short-lived trading opportunities.
4.6 SA = Sponsored Access
This refers to the practice in which banks, brokerage firms, and other financial institutions offer clients direct access to an exchange without having any pre-trade management in existence. This practice allows high-frequency traders to gain access to low latency markets with pre-execution controls that are provided by the exchange. Some of the benefits of this practice are reduced latency i.e. the delays in markets that is experienced from time to time, extra revenue opportunities, and the possibility of hitting volume discounts.
5. DIFFERENCE BETWEEN ECN, MARKET MAKER, AND STP BROKER
There are three main types of forex brokers. These are the ECN, market maker, and the STP respectively. Below are the finer details of what they specialize in and what sets them apart:
ECN, Electronic Communications Network brokers are those that employ electronic communication networks to provide their clients direct access to the other participants in the trade of currency. They differ from the two other types in their choice of infrastructure i.e. electronic as opposed to manual/conventional routes.
Market maker brokers, also called Dealing Desk brokers, are those who create markets/sales leads for their clients in return for spreads. Their role is simply to be the intermediary between the various players in the forex trading market.
STP, Straight through Processing, refers to those brokers who receive client orders and pass them directly to the liquidity providers such as banks, hedge funders, investments corporations, or other brokers. They mainly act as facilitators of the forex trading business as they themselves are not directly involved in the trade of currency.
6. WHAT IS ECN, ADVANTAGES OF TRADING IN ECN BROKER
The term ECN stands for Electronic Communication Network. An ECN broker is basically one that uses electronic communications networks as the channel/avenue through which to reach out to potential clients and reach out to the other players/participants in the currency market.
6.1 Advantages of Trading in ECN Brokers
In modern times ECN brokers are getting popular among the retails traders. In a real ECN broker, the brokers can not interrupt the trading of the trader which we may sometimes find in market maker broker. There is couple of advantages that an ECN broker has
6.1.1 Anonymity while Trading
Trading on an ECN platform is largely anonymous in nature i.e. takes place with the identity of the traders largely withheld from the other players. This brings along several benefits such as the elimination of bias while striking deals, neutral pricing, unparalleled privacy, the maximum safety of funds/financial transactions, the reflection of the real market conditions at all times, and quick dissemination of any breaking financial news. It is, therefore, the surest way of deriving maximum returns as well as exploiting full potential.
6.1.2 Variable Spreads
In other platforms, spreads (profits that forex brokers derive from their trade) are largely fixed and inflexible by virtue of being pegged on the conventional or standard currency pair. This is not the case with ECN trading platform though. This is because the prices in the ECN platform are largely based on the forces of demand, supply, and volatility. Consequently, the amount of spread that a trader may accrue out of the use of this platform is largely variable and generally higher than those derived by traders in other platforms.
6.1.3 Enhanced Execution
Executing an order or sealing a sales deal is generally quicker on this platform as compared to the other platforms. This is due to two factors. The first is the fact that no intermediaries are involved at all, which means that traders communicate and deal directly with clients. Second is the fact that the platform is largely automated, meaning that data and other relevant pieces of information are transmitted in real time. This has the attendant benefit of added convenience to the various stakeholders.
6.1.4 Trade Continuity
This platform or mode of trading eliminates any inconveniences, downtimes, and delays in the course of trading. Moreover, it is also usable on a round-the-clock basis as it is not subject to the limitations of the other modes of forex trading. The use of this platform is therefore very convenient, timely, and lucrative in the sense that it allows for the execution of numerous transactions at any given time.
6.1.5 Unlimited Client Liquidity Access
ECN platform grants brokers and other players in the field of forex trade unlimited access to the global pool of liquidity which is almost infinite as compared mainly to the local/national pool. A trader who opts to carry out his trade via the ECN platform, therefore, has strategic competitive and stronger financial muscle power over and above the other competitors who embrace other platforms.
Pros and Corns of ECN Broker
| ECN Brokers | |
| Pros | Cons |
| Direct and Accurate Price Rates from interbank | Dynamic spreads – you don’t know what the spread will be when you enter a trade. Variable Spread – A trader cannot know what the spread will be when open a trade. |
| Very Tight and Accurate Spreads | Re-quotes and order rejections. |
| The broker does not trade against you. | Limited leverage |
| The broker cannot bankrupt themselves through trading against its clients. | Rollover fees. It may go against you. |
7. What Types of Broker is Suitable for Trading
This is a common question of forex trader that which broker is suitable for them. Actually, it depends on the individual trader and their way of trading. Every broker has some advantages and disadvantages. As a trader, you need to be careful that the broker is suited your trading style. As example a scalper or short term trader may choose market maker broker as they have fixed spread On the other hand a long term of technical trader or long term may choose ECN or STP broker for best trading experience.
8. FOREX BROKER REGULATIONS
Before going to identify an honest forex broker, a trader should have sound knowledge about the regulations of forex broker. This will help choice to make right choice to go ahead.
Various countries, jurisdictions, or economic blocs have put n places various pieces of regulations that are designed to govern the trade of foreign currencies. Below is but a sample of them:
8.1 US Regulations
In the United States, forex regulation entails the provision of the necessary licenses to eligible brokers in order to conduct forex trading business after thorough due diligence; enforce the required adherence to the prevailing capital requirements; combat fraud, and enforce detailed record-keeping and reporting requirements as concerns all transactions and other related business activities. All the regulatory provisions are administered by the National Futures Association (NFA) and the U.S Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC).
Finer details regarding US regulations may be accessed by downloading the following file: http://www.nfa.futures.org/NFA-compliance/publication-library/forex-regulatory-guide.pdf.
8.2 EU Regulations
Owing to the segmented nature of the European financial sector, the tasks of regulating forex brokerage falls on the individual nation within the bloc. Examples of these regulatory bodies include Austria - Financial Market Authority (FMA), Financial Supervision Commission of Bulgaria (FSC Bulgaria), Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission CySEC, Danish Financial Supervisory Authority (Danish FSA), and the Malta Financial Services Authority (MFSA). All these individual bodies are in turn coordinated and supervised by the Markets in Financial Instruments Directive or MiFID.
8.3 Others Regulation
Other economic blocs around the world also have their own forex broker regulation regimes and regulatory bodies. To mention but a few, these include the Korean Foreign Exchange Controls and Securities Regulations, Japan Financial Services Agency (JFSA), Financial Futures Association of Japan (FFAJ), and The State Administration of Foreign Exchange (SAFE) of the People's Republic of China. They basically license forex brokers, ensure fair play, safeguard the wider public against any dangers, and settle disputes between the various parties.
8.4. LISTS OF TRUSTED REGULATORY BODIES
In order to level the playing field among the various stakeholders in the forex brokerage industry and to also safeguard the public against any potential dangers that may arise out of the trade of foreign currencies, the sector has to be heavily regulated. The following are some of the top regulators in various jurisdictions worldwide:
8.4.1 United States: National Futures Association (NFA) and Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC)
National Futures Association (NFA) is a not-for-profit, independent, self-regulatory organization for the United States derivative industries which include on-exchange traded futures, over-the-counter derivatives, and retail off-exchange foreign currencies. It is financed entirely by membership dues and is headquartered in Chicago City.
The U.S Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) on the other hand is an independent agency of the government of the United States that was created in 1974. It regulates futures and options markets and basically exists to foster transparent, open, competitive, financially sound markets in order to safeguard the US public from systemic risks, fraud, manipulations, and other abusive practices.
8.4.2 United Kingdom: Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) and Prudential Regulation Authority (PRA)
The Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) is an independent UK financial regulatory body that is mainly financed by the fees levied on the members of the financial service industry. It regulates financial firms and upholds the integrity of the financial markets of the United Kingdom.
The Prudential Regulation Authority (PRA) on the other hand is wholly owned by the Bank of England and is tasked with the responsibilities of the regulation and supervision of banks, credit unions, building societies, investments firms, and insurers. It does so by setting standards and supervising financial institutions at the level of individual firms.
8.4.3 Australia: Australian Securities and Investment Commission (ASIC)
It is an independent government body which is solely responsible for the regulation of financial services/institutions in Australia. Its core mandates are to enforce and regulate companies and financial service laws in order to protect Australian consumers, creditors, and investors. It was established on July 1, 1998 and its authority is determined pursuant to the Australian Securities and Investments Commission Act of 2001.
It is generally responsible for enforcing whole or parts of the following pieces of legislations:
• Corporations Act, 2001
• Insurance Contracts Act, 1984
• National Consumer Credit Protection Act, 2009
8.4.4 Switzerland: Swiss Federal Banking Commission (SFBC)
This Swiss-government body is primarily responsible for the regulation of the financial sector. This entails the supervision of insurance companies, banks, stock exchanges, securities dealers, and other financial intermediaries within Switzerland. It is independent of the executive arms of Swiss governments (both at the Federal and Canton levels) and reports directly to the Swiss parliament.
8.4.5 Germany: Bundesanstalt für Finanzdienstleistungsaufsicht (BaFin)
Bundesanstalt für Finanzdienstleistungsaufsicht (Deutsche/German) translates to The Federal Financial Supervisory Authority (English). It is the financial regulatory authority of the Federal Republic of Germany. It was established as an independent institution by the federal government to oversee the activities of around 2,700 banks, 700 insurance companies, and 800 other financial institutions. It is supervised by the Federal Ministry of Finance and s headquartered in Frankfurt and Bonn.
8.4.6 France: Autorité des Marchés Financiers (AMF)
Autorité des Marchés Financiers (AMF) stands for “Financial Markets Regulator” in English. It is an independent public body that regulates stock markets, safeguards investments, oversees the trade in financial instruments, furnishes investors with the necessary pieces of information, and maintains order in financial markets throughout France. It was established by the Financial Security Act of August 1, 2003 and falls under the European regulatory body of the Markets in Financial Instruments Directive (MiFID).
8.4.7 Canada: Autorité des Marchés Financiers (AMF)
It is the official financial regulatory body in the French-speaking Canada. It is headquartered in Quebec City, Canada and regulates the province’s financial markets, provides assistance to the consumers of financial products and services, enforces the laws that govern the regulation of the financial sector, and oversees the activities of insurance companies, deposit institutions (except banks), securities, and the distribution of financial services and products. It coordinates its activities in conjunction with other self-regulating bodies within Canada such as the Chambre des services financiers (Chamber of Financial Security) as well as the Chambre de l'Assurance de dommages (Chamber of Damage Insurance).
9. WHAT OTHER FACTORS YOU NEED TO KNOW
Several factors ought to be considered while shopping out for a trusted broker to trade in. A few of those factors are discussed here below:
9.1. Data Security
It refers to how secure or private a data is. It is mainly guaranteed by the application of a series of digital privacy measures to prevent unauthorized access to computers, networks, websites, and databases. Examples of these digital privacy measures include:
9.1.1 SSL
The abbreviation SSL stands for Secure Sockets Layer. It is basically a protocol (formal set of rules, standards, policies, formats, and procedures which are used to define communications between two or more devices connected to a network) which creates secure connections between a client and a server over which to send information. It uses cryptographic system comprising two keys to encrypt data. The first key is basically a private/secret key which is only known to the recipient of the message whereas the second key is public in the sense that it is known to everyone. SSL security is a must for all forex brokers in case their integrity/credibility is to be assured.
9.1.2 Two-factor Authentication
Also called "multifactor authentication", it is an extra layer of security that requires an extra piece of information such as physical token over and above the common username and password before granting access to the network or database. This provision/technology allows foolproof data integrity by making it almost impossible for intruders to gain access to computer systems, database, or network. The ideal forex broker has to have such a system installed in place.
9.1.3 Privacy Policy
It is a set of laws, rules, regulations, and standards that govern the gathering, usage, disclosure, and management of a client’s data. A trusted broker must have very stringent privacy policy which has to be adhered to the letter. It is only through this, that the privacy of the clients and the confidence of the wider public may be won/assured.
9.2. Spread Commission and Fees
Some forex brokers may charge commissions. Apart from commission, some forex brokers may also charge other hidden fees. In case such charges exist, the end result is usually a surge in the cost of accessing foreign exchange and other services provided by forex brokers. It therefore goes without saying that the trusted broker has to be as cost-effective as is practically possible in order to eliminate unnecessary financial burdens from the seekers of these financial services. If possible, the broker of choice has to provide discounts, special offers, and promos from time to time in order to lessen the financial burdens on the part of the clients.
9.3. Trading Platform
It refers to the avenue through which a broker reaches out to potential clients. The following are but a few of them:
9.3.1 Meta Trader
This is an online electronic trading platform that is extensively used by online retail foreign exchange speculative traders. It was developed and released by the MetaQuotes Software in 2005 and is licensed to foreign exchange brokers that provide it to their clients. It comprises both a client and a server component. Its server software is run by the broker whereas its client component is provided to the broker’s customers who in turn use it to stream live prices, charts, and other data besides placing orders, and managing their accounts.
9.3.2 Web-based Trading
Also called online trading, it entails the use of the internet/world wide web platform to place orders, buying or selling commodities, ordering financial securities, or exchanging currencies. This is carried out by the use of a broker’s internet-based proprietary trading platform. Its strengths lie in the facts that it is very fast, efficient and relatively inexpensive. Moreover, it requires no paperwork at all, as there is absolutely no need to fill out any forms and archive them in files or other storage media.
9.3.3 Social Trading
It is the process by which online investors rely on the user-generated financial contents that are gathered from various Web 2.0 applications as the main information sources for the making of financial decisions. This form of trading allows financial data to be analyzed, and comparisons between various copy trades, strategies, and techniques to be made with ease. The platform also grants traders the leeway to integrate their investments with decision-processes and social indicators from trading data feeds of the other traders.
9.3.4 Mobile Trading
The term “Mobile Trading” refers to the use of wireless technology in buying or selling securities. It allows investors to access trading platforms from their cell phones instead of being confined to traditional/conventional trading methods via the computers. It also allows Smartphone users to seamlessly manage their portfolios in real time i.e. even when they are located far away from their desktops/laptops.
PS: The choice of which broker to work with rests squarely on a user’s convenient trading platform.
9.4. Account Options
It is a privilege that is granted by one party to another which gives its recipient the right, but not the obligation to buy or sell stock at an agreed-upon price within a specified time-frame. Below are some of the major account options:
9.4.1 Currency Pair/ Base currencies
The currency pair is a quotation and pricing structure of the currencies that are traded in a forex market. The value of a currency is determined by the comparison of its value to that of another currency. The first-listed currency in the pair is called the base currency whereas the second is the quote currency.
The base currency, on the other hand, is the currency against which the exchange rates are generally quoted in any country. For instance, in the quote: JPY/USD, the Japanese Yen is the base currency, whereas the US Dollar is the quote currency.
9.4.2 Account Type
There are three types of brokerage accounts, namely cash, margin, and options account. They are explained in details below:
• Cash Account: In this account, the client must first of all pay in full the amount due on any transaction by the settlement date. All the money and securities in this account are registered in and entirely owned by the client, not the broker.
• Margin Account: This allows the clients to borrow money or any other security from a broker-dealer in order to gain greater leverage on their transactions. The client has to be informed of all the associated risks by the broker-dealer prior to the execution of any borrowing.
• Option Account: It is a special kind of margin account that is approved by a broker-dealer for the purposes of trading on the CBOE (Chicago Board Options Exchange). It is opened only in case the broker-dealer has sufficient proof that the client has enough net worth and that he is sophisticated enough to invest.
9.5 Trade Execution Speed
It is the pace at which a security is bought or sold in a forex market. It is very significant because the value of currencies fluctuates rapidly. Any delay in executing a trade may usually have the impact of denying the client the privilege of deriving maximum returns on the investment. The ideal/trusted broker should, therefore, have a very powerful router that has the capability of relaying the information, data or signals as fast as possible.
9.6 Spread
Spread is the difference between the bid price and the asking price of a security or an asset. It is this difference that creates the incentive for brokers and other players to stay in the foreign currency exchange business. The broker of choice must, therefore, be one who guarantees a higher spread as possible to widen the profit margin and to ensure a consistent revenue inflow. It is necessary to conduct some survey/due diligence on the various brokers available to ascertain this information.
9.7 Leverage
This is the ratio/parity of the size of a transaction to the actual investment used for margin. It allows clients to trade without necessarily putting up the full amount, with only a margin being required. For instance, a 50:1 leverage which is also known as 2% margin requirement means that a $2,000 worth of equity is required to purchase an order that is worth $100,000. As a general rule, the lower the leverage the safer the investment is, and vice versa.
9.8 Deposit and Withdrawal Process
These are the methods/various and means through which funds may be deposited into or retrieved from a forex account. There are three main methods, explained here below:
• Debit/Credit Cards – Entails the use of debit and credit cards such as bank ATM cards, Visa, and Mastercard to either deposit or withdraw funds.
• Wire Transfer – It is the real time gross bank settlement funds transfer system. It goes by various names such as SWIFT (Society for the Worldwide Interbank Funds Transfer) and Fed Wire.
• Online Payment Platforms – It is the use of online payment platforms such as PayPal, Money bookers, and Skrill to deposit or withdraw funds.
9.9 Customer Service
The customer service department is often the first point of contact between a forex broker and the wider public. It, therefore, goes without saying that the manner in which the department treats prospective clients has a strong bearing on the possibility of their response/conversion. Ideally, the customer service department has to be very polite, respectful, passionate, caring, and proactive, by making consistent follow-ups. In addition to that, the forex broker should send out newsletters, e-mail updates, and other periodicals to existing and prospective clients to keep them posted of the latest developments.
8. How to Identify Scam Brokers?
BOTTOM LINE
The entire subject matter of, “A Comprehensive Guide to Forex Brokerage” is pretty wide and complicated as is clearly deducible from the foregoing discussions. In order to take the guesswork out of the search and utilization of this critical resource, the intervention of a professional and qualified expert is by all means inevitable.
Moreover, certain aspects of the subject matter may change without notice and in so doing, affect to a large extent the nature of the challenges that would-be clients may confront. It is therefore strongly recommended that prospective utilizers of this critical resource conduct thorough research or seek professional advice prior to embarking on the task of utilizing the same.